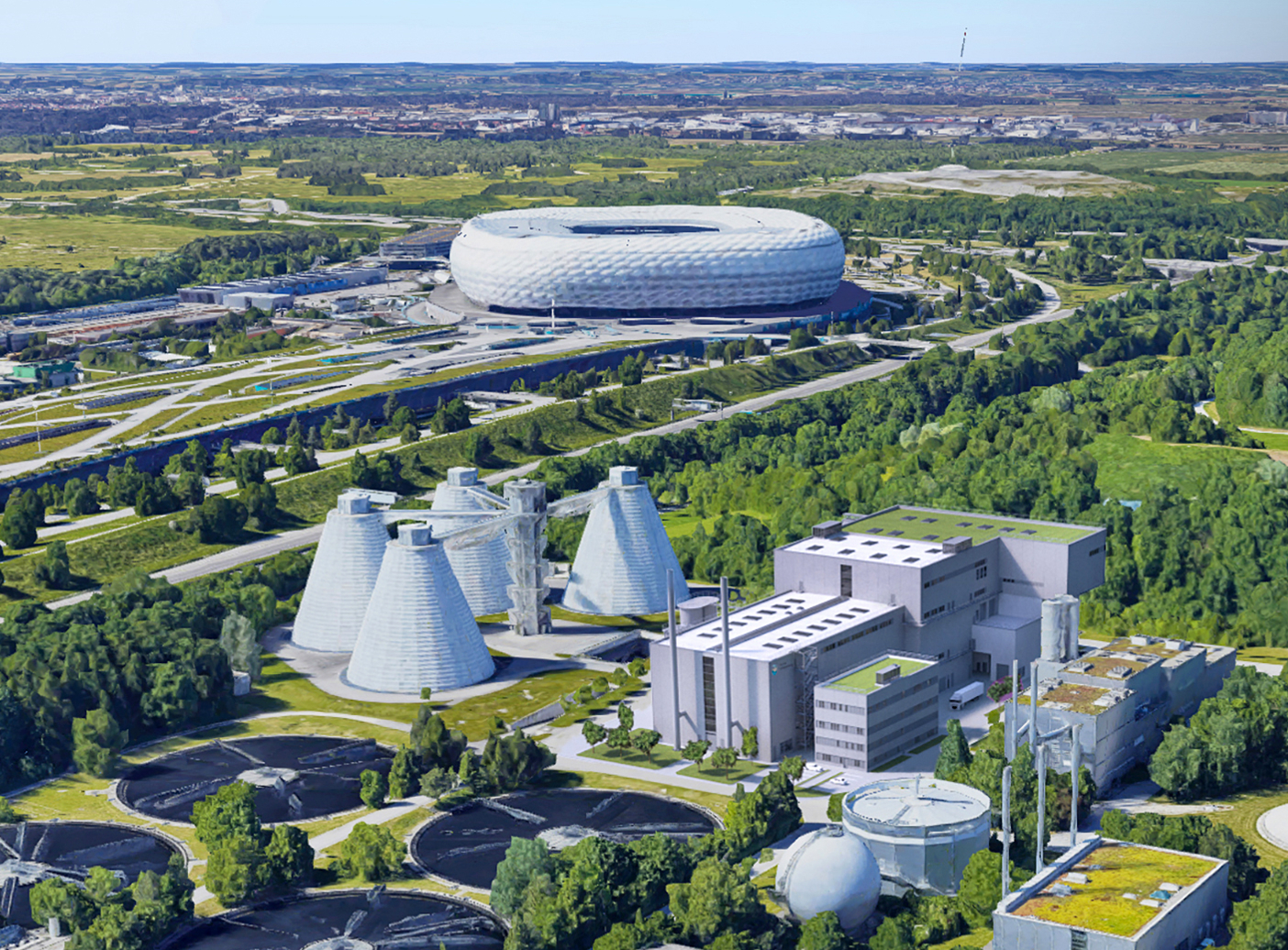
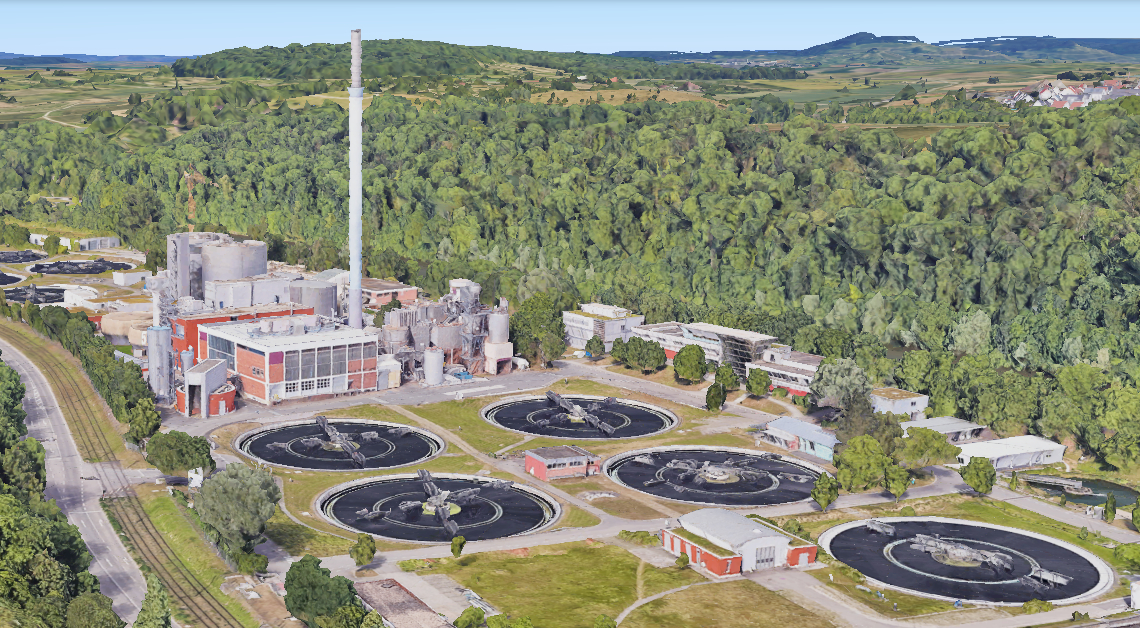
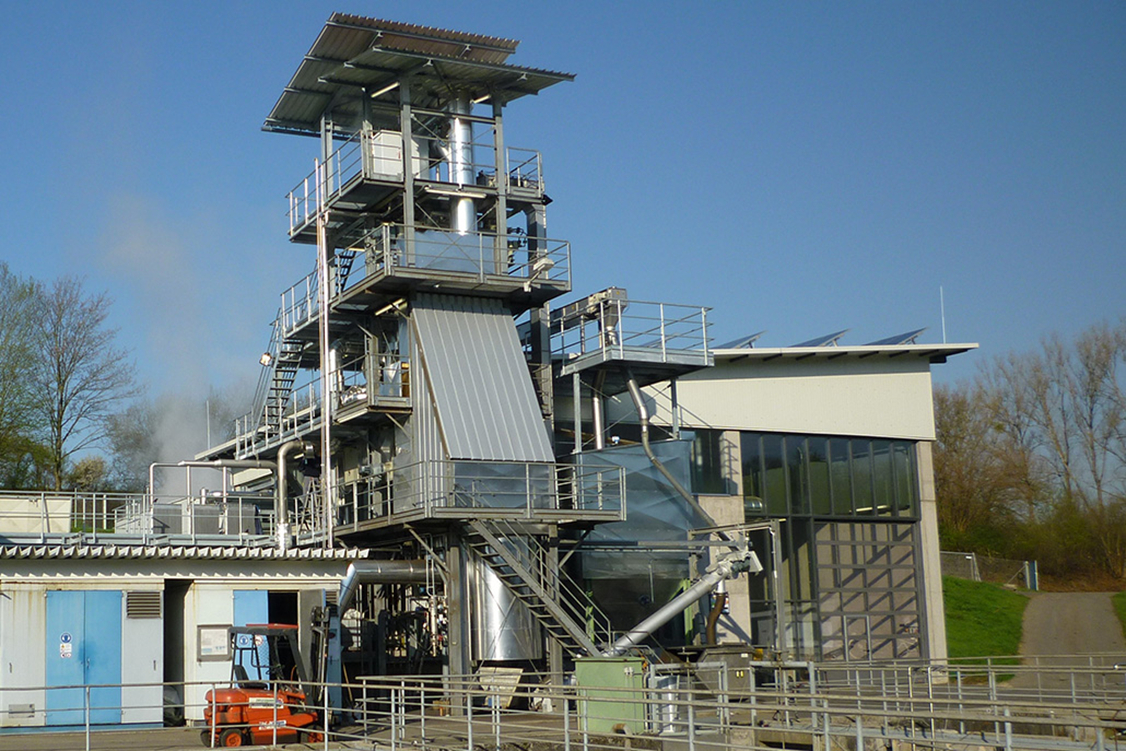
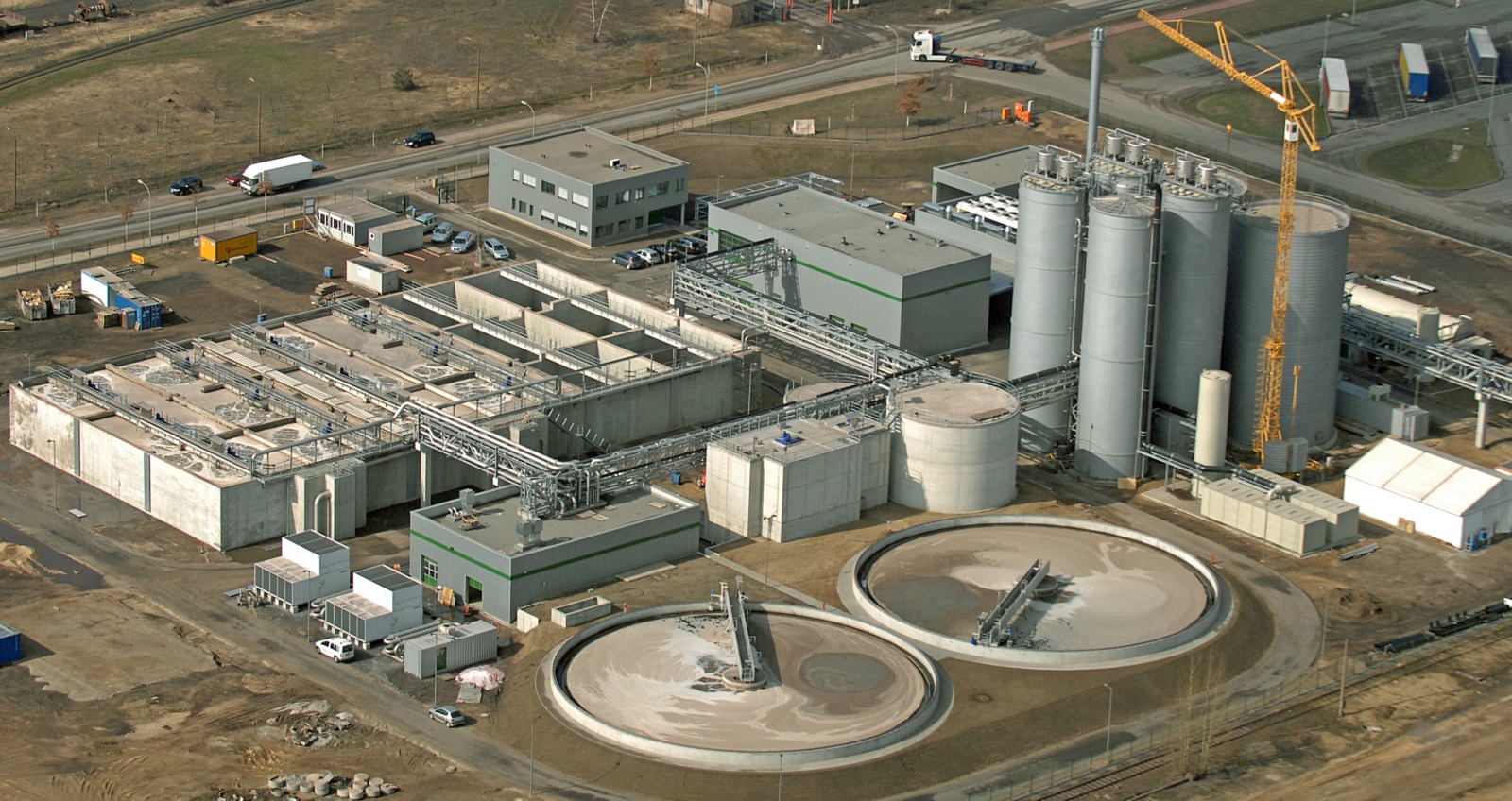
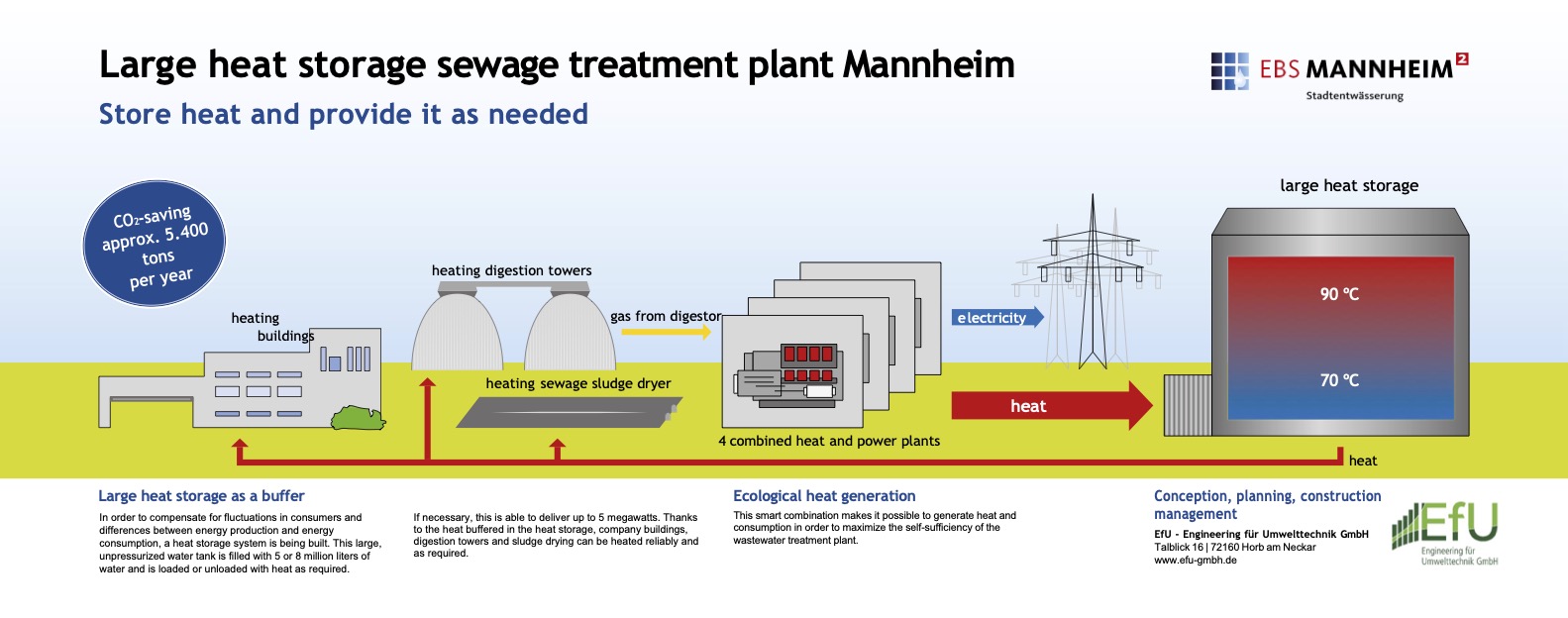
The Benefits of Treating Sewage Sludge
Sewage sludge, a byproduct of wastewater treatment, contains organic matter, nutrients, and potential contaminants. Proper treatment of sludge offers several benefits, particularly in mitigating health and environmental hazards associated with untreated waste.
Health Hazards of Untreated Sewage Sludge
Untreated sludge can harbor pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and parasites, posing serious health risks if it contaminates water supplies or food crops. Toxic heavy metals, such as lead and mercury, may also accumulate in untreated sludge, leading to long-term health issues like organ damage or neurological disorders when exposure occurs.
Environmental Hazards of Untreated Sludge
When untreated sludge is improperly disposed of, it can leach harmful substances into soil and water systems, disrupting ecosystems. High concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus can cause algal blooms in water bodies, depleting oxygen levels and killing aquatic life. Additionally, methane emissions from decomposing sludge contribute to climate change.
Benefits of Treatment
- Pathogen Reduction: Sludge treatment eliminates harmful microorganisms, making the material safer for handling and reuse.
- Resource Recovery: Treated sludge can be converted into biogas, heat, electric power and under specific circumstances also fertilizer.
- Environmental Protection: Proper treatment prevents soil and water contamination, protecting ecosystems and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Treatment ensures adherence to environmental standards, avoiding fines and promoting public health.
By treating sewage sludge, communities can turn waste into valuable resources while minimizing health and environmental risks, contributing to a more sustainable future.